How Chinese gangs are laundering drug money through Vancouver real estate
Criminal syndicates that control chemical factories in China’s booming Guangdong province are shipping narcotics, including fentanyl, to Vancouver, washing the drug sales in British Columbia’s casinos and high-priced real estate, and transferring laundered funds back to Chinese factories to repeat this deadly trade cycle, a Global News investigation shows.

The flow of narcotics and chemical precursors — and a rising death count in western Canada caused by synthetic opioids — is driven by sophisticated organized crime groups known as Triads.
The Triads have infiltrated Canada’s economy so deeply that Australia’s intelligence community has coined a new term for innovative methods of drug trafficking and money laundering now occurring in B.C.
It is called the “Vancouver Model” of transnational crime.
LISTEN: Investigative reporter Sam Cooper explains the “Vancouver Model’ of transnational crime
B.C. Attorney General David Eby has reviewed the report, and recently travelled to Ottawa to inform a federal committee of his concerns. His message was blunt. Eby testified that Canada’s anti-money laundering system has completely failed. He told the committee that gangsters have been openly carrying hockey bags stuffed with hundreds of thousands in drug cash into B.C. casinos, and there has not been a single prosecution.
In an interview with Global, Eby said the Australian report shows “that Vancouver is now recognized internationally as a hub of transnational money laundering.”
Langdale’s report explains how Chinese criminals exploit “weak links” in global regulation. In one example, Triads deal with the state of North Korea, and Latin American drug cartels, to run a shadow economy based on the trading of narcotics, counterfeit goods, and illegal migrants.
Similarly, the regions of Vancouver, Hong Kong and Macau have formed a black market financed by intricate Chinese underground banking networks. According to the Vancouver Model report, the underground banks are at the heart of Chinese drug trafficking crime.
These secret banks have developed for centuries on China’s southern coast, police intelligence reports say. They consist of family members spread across Chinese communities worldwide. They can move money, drugs and commodities around the world, without having to send funds across national borders. The banks maintain reserves of various currencies at locations worldwide, taking deposits in one area, and paying out withdrawals in another.
In order to function, the underground banks need financial facilitators, and the Triads have used some lawyers, bankers, casino operators, and gambling junket operators in Hong Kong, Macau and Vancouver, Langdale’s report says.
LISTEN: B.C. Attorney General David Eby responds to money laundering concerns
The VIPs can cash out chips to buy global real estate. They pay back gambling loans in China, with small interest fees, allowing them to illicitly send legitimate wealth abroad, or launder ill-gotten gains. The junket lenders have migrated from Macau to Vancouver casinos, B.C. government documents show, bringing many VIP gamblers with them.
Langdale says that Australia’s government is worried about Chinese capital flight, because Austrac can’t differentiate between legitimate and criminal money pouring into Australian assets. His report outlines a worst case for Australia: “Possible scenario. Sydney as a regional hub for Chinese transnational crime (the Vancouver Model.)”
The model’s criminal elements, according to the report, are:
- “Traffic illegal drugs from Guangdong and Latin America”
- “North American illegal drug dealing networks supplied by Chinese methamphetamines and precursor chemicals”
- “Launder money into high-end real estate (funded by Chinese) capital flight, and launder money through the high-roller tables in casinos”
- “High rollers used Canadian casinos, junket operations, and investment in Canadian real estate”
- “Use banks, money transfer businesses to shift money to and from China and other countries (including) Mexico and Columbia.”
WATCH: B.C. Attorney General David Eby explains how transnational crime groups target Canada
The world’s factory
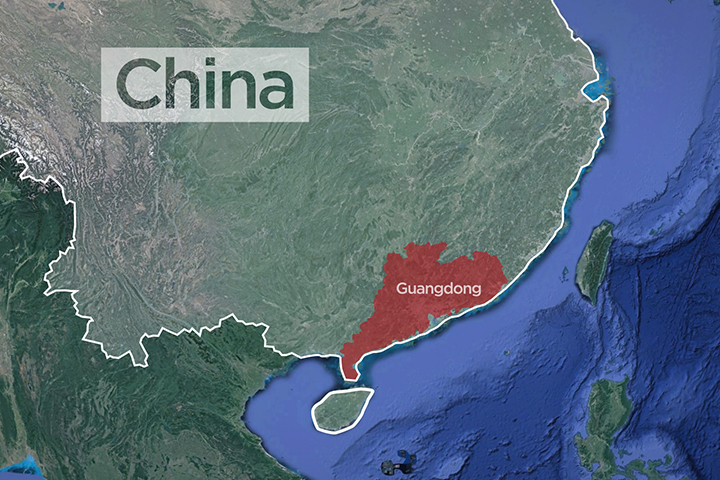
Langdale’s research focuses on the global supply of illegal drugs and crime from Guangdong, a province that faces the South China Sea, and borders China’s special administrative regions, Hong Kong and Macau.
Guangdong is China’s most populous province, with 100 million citizens, including about 30 million migrant workers, and the most billionaires in China. The province’s economy is powered by the industrial Pearl River Delta region, which includes cities such as Zhuhai and Shenzhen. And with massive shipping infrastructure that connects with major international ports, Guangdong is known as the “world’s factory,” Langdale says.
It is also the world’s factory for chemical opioids.
“Guangdong is a good location for production and trafficking of illegal goods and services,” the report says, with its proximity to Hong Kong and Macau, and their “well-established networks of facilitators skilled at shifting money overseas via offshore banking and finance.”
“You have a confluence of a major financial market in Hong Kong beside this seething mass of capitalism,” Langdale said in an interview.
Command and Control
According to U.S. and Canadian law enforcement, illegal shipments of fentanyl from Chinese factories and fentanyl overdose deaths in North America are multiplying at an exponential rate.
Last October, the U.S. Dept. of Justice announced a major drug-trafficking and money-laundering investigation against two Chinese men, who are alleged to have had “command and control” of numerous chemical factories and labs in southern China, used to ship “massive quantities of deadly fentanyl and other synthetic opioids to communities throughout the United States.”
It was the first time the U.S. labelled Chinese nationals as top priority international crime targets, on a level with Colombian drug cartel kingpins.
In a separate case last December, Chinese state news agency Xinhua reported that Chinese police arrested 19 suspects accused of manufacturing fentanyl from Guangdong factories and sending the drugs to North America.
And Canada Border Services Agency documents say seizure amounts of fentanyl from China have surged since three years ago, with 7.2 kilograms seized in 2014, that rising sharply to 58 kilograms in 2015, and 20.5 kilograms seized in the fiscal year of 2016-2017.
Meanwhile, the B.C. Coroners Service reported more than 1,400 people died of an illicit drug overdose in the province in 2017, with about 81 per cent of the deaths involving fentanyl, that was most often mixed with heroin, cocaine or methamphetamines. It was the most overdose deaths ever in B.C.
In his 34-year policing career former RCMP superintendent Garry Clement served as director of the Proceeds of Crime program, an undercover investigator, and from 1991 to 1994, as liaison officer for Canada’s Hong Kong embassy.
He is a certified consultant on financial and organized crime, and has been an expert witness in numerous money-laundering trials.
In fact, Clement investigated and reported on this same criminal blueprint, in 1994. In Canada’s Consulate General in Hong Kong, Clement and an immigration control officer uncovered a Triad immigration fraud that they say allowed the gangs to gain a foothold in B.C.
To grasp the Vancouver Model of Triad crime, Clement says, some Chinese economic and historical understanding is needed.
In his 1994 report, Triads and other Asia-based Organized Crime, Clement writes that prior to China’s communist revolution, the Triads had deep connections to military and political leaders. A Chinese president himself, Chiang Kai-Shek, was a Triad associate who staffed his army with opium-trading gangsters, Clement’s 1994 report says.
When Chairman Mao and the communists seized control of Mainland China in 1949, many Triads fled to Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan. Hong Kong was substantially built on British opium trading fortunes, Clement’s report says, and provided many business opportunities for the Triads.
Meanwhile, Mao and the communists claimed to have cleansed Mainland China of drug vice. But the Triads were allowed to return. In the 1980s, a new Chinese leader, Deng Xiaoping, ushered in economic liberalization, with a strong focus on factories and global exports in Guangdong.
Deng’s model of reform tolerated corruption between state officials and business tycoons for the sake of rapid job growth.
According to Clement, famous sayings credited to Deng — such as “it doesn’t matter whether a cat is black or white as long as it catches mice,” and “not all Triads are bad” — explain how crime syndicates gained control in Guangdong.
Vancouver Model real estate laundering
After establishing a strong base in Vancouver, Clement says, the Triads forged a criminal trade loop with Triad factories in Guangdong.
Clement’s 1994 report explains how the Triads have used “quasi-legitimate” real estate development, construction, and financial companies to launder drug cash in Vancouver real estate. In one method, Triad companies send drug funds to offshore bank accounts, and use these deposits to secure mortgages for purchasing and developing B.C. land.
Another method involves falsified contracts used to make drug cash appear to be legitimate real estate wealth. The buyers pay artificially high prices for property, recording transactions in B.C.’s land title system. But a much lower actual price is paid to a Triad-linked seller, in an offshore bank account transaction.
Clement says these offshore transactions have likely had the effect of artificially inflating prices across Metro Vancouver housing markets, and leaving swaths of empty homes.
“What we see in Vancouver real estate is heartbreaking,” Clement said. “I saw the same thing in Panama, with the empty homes.”
Guangdong-Hong Kong-Vancouver-Sydney
Langdale’s report says that transnational criminals in Mainland China and Hong Kong play different roles in the Vancouver Model. The Guangdong Triads specialize in large-scale production of chemical narcotics, as well as counterfeit products. They are also involved in wildlife smuggling and human trafficking.
The Hong Kong Triads specialize in financing drug shipments, as lenders and insurers. They are involved in loan sharking, stock market manipulation, and criminal money laundering services. These Triads show some of the same characteristics as suspects named in B.C. Lottery Corp. investigation documents.
The Hong Kong syndicates also re-route shipments of counterfeit products from North Korea, such as tobacco, Langdale’s report says. CBSA documents say that counterfeit tobacco from Chinese and Hong Kong ports often ends up in B.C.
A review of B.C. government documents obtained by Global News shows that a Chinese man linked to Vancouver casino junket lenders was cited in a major tobacco trafficking investigation.
The man, who is allegedly involved in criminal real estate lending networks in Vancouver, has defaulted on $196,000 in payment of “taxes, penalty or interest,” under the Tobacco Tax Act, a 2010 B.C. Supreme Court filing says.
Meanwhile, some of the Chinese VIP gamblers identified in B.C. Lottery Corp. documents obtained by Global News, are alleged to be involved in B.C. wildlife trafficking cases. B.C.’s Ministry of Environment would not disclose documents about these cases, citing potential harm to police investigations.
The Mainland China Triads also have the ability to trade illegal migrants around the world, Langdale says. CBSA documents obtained by Global point to a case of forged documents that likely is connected to Triad schemes, Clement said.
The documents say that in April 2016, border agents at a Montreal airport seized about 5,600 counterfeit foil holograms from China, designed to authenticate Quebec health insurance cards. This case concerns the CBSA, an intelligence brief says, because the forgeries could facilitate immigration frauds that threaten Canada’s national security.
In an interview, Langdale said that in the Vancouver Model, Triad crime money will ultimately flow back into Chinese factories that produce deadly narcotics, and the export cycle will continue. But the Triad money will also taint economies worldwide.
“The recycling (of dirty cash) may take place in Australia, Vancouver, Hong Kong’s offshore money market, or Shenzhen, depending on where they see the greatest opportunities for their money,” Langdale said. “It could also go into legal enterprises. Overall, the economy becomes totally corrupted by a web of licit and illicit activities.”
Fintrac loopholes
Kim Marsh, a former international organized crime unit commander for the RCMP, now consults with international governments in efforts to detect corrupt officials and criminals seeking money laundering havens.
Marsh says that he agrees with Attorney General Eby’s conclusion, that Canada’s anti-money laundering system has failed.
Fintrac, as Garry Clement puts it, is a “Rolls Royce, without an engine.” He means that Fintrac’s reporting requirements are stringent, but reports rarely lead to investigations and enforcement.
The system requires that Canada’s financial professionals, including bankers, casino operators, realtors and currency exchange owners, report suspicious or large cash transactions. Fintrac receives extensive reports from casino operators and banks, especially.
However, Eby says that in the casino industry, ample reporting only means that operators can claim they have fulfilled their regulatory obligations. And meanwhile, he said, VIPs have the green-light to wheel suitcases stuffed with $20 bills into high-limit betting rooms.
A major problem, Marsh says, is that Canadian privacy laws block police investigators from working with Fintrac agents, and accessing Fintrac’s valuable cache of evidence.
Another problem, is Canada’s gaping lawyer loophole.
A 2016 report from Transparency International said that almost 50 per cent of Vancouver’s most expensive properties are owned through legal mechanisms, such as trusts and shell companies, which are used to hide true ownership.
Canadian lawyers won an exemption from Fintrac reporting in a 2015 Supreme Court ruling.
In 2016 the Financial Action Task Force, a partnership among international governments, recommended that Canada amend Fintrac laws to bring lawyers into the system. The task force reported that money laundering in Vancouver real estate is linked to trust account services provided by some lawyers.
ASIAN ORGANIZED CRIME THRIVING IN CANADA
When organized crime is mentioned, what comes to mind for most people is the Italian Mafia. But one of the most powerful and dangerous criminal groups is the Triads, a centuries-old Chinese crime gang that has a strong and ubiquitous presence throughout the world, including Canada.
Triad societies, with their secret initiation rituals and code of loyalty, have long overshadowed Chinese communities around the globe. As with other Asian gangs from countries such as Vietnam, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Korea, they prey upon their own, often using fear and intimidation tactics as well as outright physical violence.
Thought to be the world’s largest criminal fraternity, the Triads, or Chinese Mafia, have a long history in Canada. They initially established operations there in the 1850s, when the Chinese began arriving in North America to build the railroads and work in the goldfields. Many of the migrants—desperate to escape China after the horror of the 1850 Taiping Rebellion in which 20 million died—were brought in illegally by the Triads.
The Triads provided passage to Canada, and those who came had to work for years in low-paying jobs or as prostitutes to pay off their transportation debt, just as the many illegal aliens who have been smuggled into the country do today. Many used Canada as a jumping-off point to enter the United States, again just as they do today. Because the predominantly male Chinese population at the time was either barred from mixing with local women or did not wish to, the Triads brought in women and girls from China, some as young as 12. They also imported opium, the use of which was legal at the time, and ran gambling and prostitution houses. Before long, crime and drug addiction began to spread across the country.
In modern times, in addition to human trafficking and drug smuggling, the Triads are involved in such unsavory practices such as arms dealing, economic espionage, counterfeiting, and money laundering. Hong Kong, home to more than 50 Triad societies totalling hundreds of thousands of members, is a key transit point for the large amounts of Golden Triangle heroin and methamphetamines that flow into North America. The Triads controlled most of the drugs’ transportation.
A 2004 Criminal Intelligence Service Canada (CISC) report stated that Asian organized crime presents a major threat in Canada because of its many widespread and well-run criminal operations. CISC said Asian-based street gang violence is on the rise in several cities, and that the street gangs have connections with more sophisticated Asian organized crime groups—in other words, the Triads. At a local level, Asian gangs are involved in a long list of criminal activities: credit card fraud, luxury car theft, prostitution, home invasions, staged vehicle accidents, contract killings, assaults, welfare and employment insurance fraud, drug trafficking, software piracy, loan-sharking, and illegal gaming. While scattered from coast to coast, Asian gangs are most active in Vancouver, Calgary, Edmonton, and Toronto, the CISC report said.
Former diplomat and organized crime specialist Brian McAdam says the Triads often form an alliance with other Asian gangs, such as the Vietnamese. The Vietnamese gangs now largely control marijuana growing-operations in Canada and sometimes collude with Hell’s Angels, thought to be British Columbia’s largest organized crime group. The Vietnamese gangs, known for their extreme violence and preference of automatic weapons, often take on the dirty work at the street level for the Triad, McAdam says. “Within each Chinese community, there’s usually a strong Triad presence controlling and extorting money from the businesses, and if there’s drugs, they’re bringing them in,” says McAdam.
In addition to setting up legitimate companies in Vancouver and other Canadian cities as a front for their activities, McAdam says the Triads have in many cases been successful in compromising members of the police force as well as politicians at the federal and municipal level. He says the leaders of the benevolent societies and the Chinese Masonic temples in various Chinatowns are often Triad leaders, who may contribute large political donations as well as promise the vote of the Chinese community.
In 2003, the Asian Pacific Post reported that veteran police Superintendent Garry Clement warned Ottawa in an internal memo of shocking success by the Chinese Mafia having made connections with Canadian politicians.
In its International Crime Threat Assessment report, the U.S. government said Asian organized crime in Canada poses a security threat to the United States. The report details how Chinese criminal organizations from Hong Kong, China, Macau, and Taiwan have exploited the country’s immigration policies and entrepreneur program, and are using Canada as a base for their operations in the United States. “Canada has become a gateway for Chinese criminal activity directed at the United States, particularly heroin trafficking, credit card fraud, and software piracy,” the report stated.
James Dubro, author of Dragons of Crime: Inside the Asian Underworld, says many organized crime gangs smuggle their illegal booty through the native reserves that straddle the Canada-U.S. border in Quebec and Ontario. He says it’s difficult for police to do anything about it since those reserves have their own police force which is itself often corrupt. “Everyone uses [reserve land]—the mafia, the bikers, the Triads, the Vietnamese gangs. They all use it for people smuggling, drug smuggling and everything else.”
Worldwide, human trafficking is one of the biggest money makers for the Triads. In 2004, the Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) estimated that 600 to 800 people are brought illegally into Canada each year, and another 1,500 to 2,000 are trafficked through Canada into the United States. While some trafficking victims are pressed into forced labor, most women and children are trafficked for the purposes of sexual exploitation.
Dubro says that because many Hong Kong nationals who moved to Vancouver in the 1980s after Hong Kong was returned to China had links to organized crime, Asian gangs have become the “dominant criminal force” in British Columbia. It was in the 1980s that the Big Circle Boys, a gang largely consisting of former Red Guards who moved from China to Hong Kong after the Cultural Revolution, set up shop in Vancouver.
The Vancouver RCMP said last year that they were shifting their focus to going after the gang kingpins rather than the minor players, and to that end have compiled a list of B.C.’s 20 top crime bosses. But Dubro says when it comes to Asian gangs, because they often have connections in high places and because their most powerful members do not operate at the street level, nabbing the key players is easier said than done. “The big guys are very hard to get.”
Epoch Times Victoria Staff
Dec 06, 2006
Garry Clement
March 1st, 2022 President David Taylor of Versabank engaged Garry Clement to become their Chief Compliance Officer. Additionally, Garry became a member of the Board of Directors for a new financial institution in Barbados where his financial/compliance background is being relied on.
Financial Crime Prevention expert and advocate Garry Clement joined the Association of Certified Financial Crime Specialists team in 2016 as the Executive Vice President and helped lead strategic changes until April 2018 at which time he transitioned back to a Senior Advisor to the Chairman of Barbri (ACFCS) until April 2019.
Following this he and again took a hands-on role with his company Clement Advisory Group. Garry has over 34 years of financial crime experience.
Garry Clement relies on his 34 years of policing experience, having worked in roles as the National Director for the RCMP’s Proceeds of Crime Program, working as an investigator and undercover operator in some of the highest organized crime levels throughout Canada. During Garry’s policing career, he received numerous awards and commendations for his investigative abilities, inclusive of recognitions from the US Drug Enforcement Administration and the CIA.
Garry has authored and/or co-authored several papers in national and international publications on organized crime and money laundering. Garry’s experiences make him an excellent, highly entertaining speaker for conferences, seminars and training programs.
Garry began working in the anti-money laundering arena in 1983, and was one of the pioneers of the RCMP’s proceeds of crime program. Since 2007 he has worked as a consultant with a focus on financial crime and independent money laundering reviews for the money service business industry, credit unions and securities firms. These roles provided Garry with experience in the areas of organized crime, drug trafficking, international smuggling and money laundering.



No comments:
Post a Comment
Comments always welcome!