Jesuit China Missions; The First Jesuit To Try And Reach China Was Francis [Xavier]!
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 |
Francis Xavier (left), Ignatius of Loyola (right) and Christ at the upper center. Below: Matteo Ricci (right) and Johann Adam Schall von Bell (left), all in dialogue towards the evangelization of China.
|
 |
| A world map in Chinese (Wanguo Quantu 萬國全圖, lit. "Complete map of all the countries"), developed by the Jesuits, early 17th century.[1] |
The first attempt by the Jesuits to reach China was made in 1552 by St. Francis Xavier, Spanish priest and missionary and founding member of the Society of Jesus. Xavier never reached the mainland, dying after only a year on the Chinese island of Shangchuan. Three decades later, in 1582, Jesuits once again initiated mission work in China, led by several figures including the Italian Matteo Ricci, introducing Western science, mathematics, astronomy, and visual arts to the Chinese imperial court, and carrying on significant inter-cultural and philosophical dialogue with Chinese scholars, particularly representatives of Confucianism. At the time of their peak influence, members of the Jesuit delegation were considered some of the emperor's most valued and trusted advisers, holding numerous prestigious posts in the imperial government.
Many Chinese, including notable former Confucian scholars,[vague] adopted Christianity and became priests and members of the Society of Jesus.
According to research by David E. Mungello, from 1552 (i.e., the death of St. Francis Xavier) to 1800, a total of 920 Jesuits participated in the China mission; of whom 314 were Portuguese, and another 130 were French.[2] In 1844 China may have had 240,000 Roman Catholics, but this number grew rapidly, and in 1901 the figure reached 720,490.[3] Many Jesuit priests, both Western-born and Chinese, are buried in the cemetery located in what is now the School of the Beijing Municipal Committee.[4]
Contents |
The Jesuits in China
The arrival of Jesuits
 |
| Matteo Ricci (left) and Xu Guangqi (right) in the Chinese edition of Euclid's Elements published in 1607. |
 |
| Nicolas Trigault (1577-1629) in Chinese costume, by Peter Paul Rubens. |
The first Portuguese explorer credited with reaching China was Jorge Álvares in 1513. Unlike the early European travelers of the 14th and 15th centuries, who reached China overland by traveling thousands of miles through Mongol- or Muslim-controlled territory, during the Age of Discovery of the 15th to 17th centuries Europeans started arriving on China's southeastern coast in their own boats, from Portuguese-controlled Malacca or the Spanish Philippines.
Fairly soon after the establishment of the direct European maritime contact with China (1513) and the creation of the Society of Jesus (1540), at least some Chinese became involved with the Jesuit effort. As early as 1546, two Chinese boys enrolled in the Jesuits' St. Paul's College in Goa, the capital of Portuguese India. One of these two Christian Chinese, known as Antonio, accompanied St. Francis Xavier, a co-founder of the Society of Jesus, when he decided to start missionary work in China. However, Xavier failed to find a way to enter the Chinese mainland, and died in 1552 on Shangchuan island off the coast of Guangdong,[5] the only place in China where Europeans were allowed to stay at the time, but only for seasonal trade.
A few years after Xavier's death, the Portuguese were allowed to establish Macau, a semi-permanent settlement on the mainland which was about 100 km closer to the Pearl River Delta than Shangchuan Island. A number of Jesuits visited the place (as well as the main Chinese port in the region, Guangzhou) on occasion, and in 1563 the Order permanently established its settlement in the small Portuguese colony. However, the early Macau Jesuits did not learn Chinese, and their missionary work could reach only the very small number of Chinese people in Macau who spoke Portuguese.[6]
A new regional manager ("Visitor") of the order, Alessandro Valignano, on his visit to Macau in 1578-1579 realized that Jesuits weren't going to get far in China without a sound grounding in the language and culture of the country. He founded St. Paul Jesuit College (Macau) and requested the Order's superiors in Goa to send a suitably talented person to Macau to start the study of Chinese. Accordingly, in 1579 the Italian Michele Ruggieri (1543–1607) was sent to Macau, and in 1582 he was joined at his task by another Italian, Matteo Ricci (1552–1610).[6]
Ricci's policy of accommodation
Ricci, Ruggieri, and their followers, had a desire of creating a Sino-Christian civilization that would match the Roman-Christian civilization of the West. Both Ricci and Ruggieri were determined to adapt to the religious qualities of the Chinese: Ruggieri to the common people, in whom Buddhist and Taoist elements predominated, and Ricci to the educated classes, where Confucianism prevailed. Ricci, who arrived at the age of 30 and spent the rest of his life in China, wrote to the Jesuit houses in Europe and called for priests - men who would not only be "good", but also "men of talent, since we are dealing here with a people both intelligent and learned".[7]A few responded, and Ricci began to train them so that they might approach the Chinese authorities, offering the court scholarly and scientific assistance. Ricci's followers had the deliberate intention of completely de-westernizing themselves, to make a Confucian adaptation of their style of life, patterns of thought, preaching and worship. Both Ricci and Ruggieri felt that it would be possible to "prove that the Christian doctrines were already laid down in the classical works of the Chinese people, albeit in disguise". Indeed, they and their followers were convinced that "the day would come when with one accord all missionaries in China would look in the ancient texts for traces of primal revelation".[8]
Tension eventually developed between Ricci and his followers and those of Ruggieri. Ricci's focus was on adapting to Confucianism and strongly rejecting Taoism, while Ruggieri's thesis was that there was a closer affinity between the Tao of Chinese thought and the incarnate Logos of the New Testament.
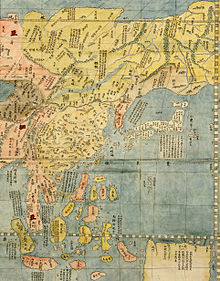 |
| Map of the Far East in 1602, by Jesuit missionary Matteo Ricci (1552–1610) |
In his diary, Ricci wrote: "From morning to night, I am kept busy discussing the doctrines of our faith. Many desire to forsake their idols and become Christians".[10] His missionary directives were explicit:
"The work of evangelization, of making Christians, should be carried on both in Peking and in the provinces… following the methods of pacific penetration and cultural adaptation. Europeanism is to be shunned. Contact with Europeans, specifically with the Portuguese in Macau, should be reduced to a minimum. Strive to make good Christians rather than multitudes of indifferent Christians… Eventually when we have a goodly number of Christians, then perhaps it would not be impossible to present some memorial to the Emperor asking that the right of Christians to practice their religion be accorded, inasmuch as is not contrary to the laws of China. Our Lord will make known and discover to us little by little the appropriate means for bringing about in this matter His holy will.[11]
 |
Represented (top): Matthieu Ricci, Adam Schaal, Ferdinand Verbiest
Bottom: Paul Siu (Xu Guangqi), colao or Prime Minister of State; Candide Hiu, grand-daughter of Colao Paul Siu. |
One time the Chongzhen Emperor was nearly converted to Christianity and broke his idols.[13]
Dynastic change
The fall of the Ming Dynasty (1644) and the conquest of China by the Manchu Qing regime brought some difficult years for the Jesuits in China. While some Jesuit fathers managed to impress Manchu commanders with a display of western science of ecclesiastical finery and to be politely invited to join the new order (as did Johann Adam Schall von Bell in Beijing in 1644, or Martino Martini in Wenzhou ca. 1645-46),[14] others endured imprisonment and privations, as did Lodovico Buglio and Gabriel de Magalhaes in Sichuan in 1647-48[15][16] or Alvaro Semedo in Canton in 1649. Later, Johann Grueber was in Beijing between 1656 and 1661. |
The Chinese Jesuit Michael Alphonsius Shen Fu-Tsung visited France and Britain in 1684-1685. "The Chinese Convert" by Sir Godfrey Kneller.
|
French Jesuits
In 1685, the French king Louis XIV sent a mission of five Jesuit "mathematicians" to China in an attempt to break the Portuguese predominance: Jean de Fontaney (1643–1710), Joachim Bouvet(1656–1730), Jean-François Gerbillon (1654–1707), Louis Le Comte (1655–1728) and Claude de Visdelou (1656–1737).[20]Travel of Chinese Christians to Europe
See also: Rabban bar Sauma
Prior to the Jesuits, there had already been Chinese pilgrims who had
made the journey westward, with two notable examples being Rabban bar Sauma and his younger companion who became Patriarch Mar Yaballaha III, in the 13th century.While not too many 17th-century Jesuits ever went back from China to Europe, it was not uncommon for them to be accompanied by young Chinese Christians. One of the earliest Chinese travelers to Europe was Andreas Zheng (郑安德勒; Wade-Giles: Cheng An-te-lo), who was sent to Rome by the Yongli court along with Michał Boym in the late 1650. Zheng and Boym stayed in Venice and Rome in 1652-55. Zheng worked with Boym on the transcription and translation of the Nestorian Monument, and returned to Asia with Boym, whom he buried when the Jesuit died near the Vietnam-China border.[21] A few years later, another Chinese traveller who was called Matthaeus Sina in Latin (not positively identified, but possibly the person who traveled from China to Europe overland with Johann Grueber) also worked on the same Nestorian inscription. The result of their work was published by Athanasius Kircher in 1667 in the China Illustrata, and was the first significant Chinese text ever published in Europe.[22]
Better known is the European trip of Shen Fo-tsung in 1684–1685, who was presented to king Louis XIV on September 15, 1684, and also met with king James II,[23] becoming the first recorded instance of a Chinese man visiting Britain.[24] The king was so delighted by this visit that he had his portrait made, and had it hung in his bedroom.[24] Later, Arcadio Huang, another Chinese Jesuit, would also visit France, and was an early pioneer in the teaching of the Chinese language in France in 1715.
Scientific exchange
 |
| Confucius Sinarum Philosophus ("Life and works of Confucius"), by Father Philippe Couplet and Father Prospero Intorcetta, 1687. |
In 1627, the Jesuit Johann Schreck produced the first book to present Western mechanical knowledge to a Chinese audience, Diagrams and explanations of the wonderful machines of the Far West.[26]
This influence worked in both directions:
[The Jesuits] made efforts to translate western mathematical and astronomical works into Chinese and aroused the interest of Chinese scholars in these sciences. They made very extensive astronomical observation and carried out the first modern cartographic work in China. They also learned to appreciate the scientific achievements of this ancient culture and made them known in Europe. Through their correspondence European scientists first learned about the Chinese science and culture.—[27]
 |
| The steam engine manufactured by Ferdinand Verbiest at the Qing Court in 1672. |
Telling Europe about China
 |
A page from Mémoires concernant l'histoire, les sciences et les arts des Chinois, 1780.
|
Since the mid-17th century, detailed Jesuits' accounts of the Eight trigrams and the Yin/Yang principles[34] appeared in Europe; soon, they attracted significant attention of European philosophers, such as Leibniz.
 |
| The 1734 map compiled by d'Anville based on the Jesuits' geographic research during the early 1700s |
In the early years of the 18th century, Jesuit cartographers travelled all over the Chinese Empire, performing astronomical observations to determine latitude and longitude (relative to Beijing) of various locations and drawing maps. Their work was summarized in a four-volume Description géographique, historique, chronologique, politique et physique de l'empire de la Chine et de la Tartarie chinoise published by Jean-Baptiste Du Halde in Paris in 1735, and a map compiled by Jean Baptiste Bourguignon d'Anville (published 1734).[35]
Chinese Rites Controversy
Main article: Chinese Rites controversy
In the early 18th century, a dispute within the Catholic Church arose
over whether Chinese folk religion rituals and offerings to the emperor
constituted paganism or idolatry.
This tension led to what became known as the "Rites Controversy," a
bitter struggle that broke out after Ricci's death and lasted for over a
hundred years.At first the focal point of dissension was the Jesuit Ricci's contention that the ceremonial rites of Confucianism and ancestor veneration were primarily social and political in nature and could be practiced by converts. The Dominicans, however, charged that the practices were idolatrous, meaning that all acts of respect to the sage and one's ancestors were nothing less than the worship of demons. A Dominican carried the case to Rome, where it dragged on and on, largely because no one in the Vatican knew Chinese culture sufficiently to provide the pope with a ruling. Naturally, the Jesuits appealed to the Chinese emperor, who endorsed Ricci's position. Understandably, the emperor was confused, as to why missionaries were attacking missionaries in his capital, and asking him to choose one side over the other, when he might very well have simply ordered the expulsion of all of them.
 |
| The French Jesuit Joseph-Marie Amiot (1718-1793) was official translator of Western languages for the Qianlong Emperor. |
The controversy raged on. In 1742 Pope Benedict XIV officially opposed the Jesuits, forbade all worship of ancestors, and terminated further discussion of the issue. This decree was repealed in 1938. But the methodology of Matteo Ricci remained suspect until 1958, when Pope John XXIII, by decree in his encyclical Princeps Pastorum, proposed that Ricci become "the model of missionaries."[citation needed]
In the intervening years the Ming Dynasty collapsed (1644), to be replaced by the "non-scholarly" and foreign Manchus. At first, the Jesuits were employed and welcome in the court of K'ang-hsi. However, when Pope Clement XI attempted to send Maillard de Tournon as an emissary to control the Jesuit Missionaries and restrict Christian tolerance and practice of Chinese Rites, the request was denied by K'ang-hsi. Further, Jesuit missionaries had to sign a document stating that they agreed to Confucian and ancestral rituals, and those who did not sign were deported. Maillard himself was imprisoned. In spite of this, the Jesuits continued to preach and work in China - but over time, the influence of the Catholic missionary orders began to wane. Pope Clement XIV dissolved the Society of Jesus in 1773. The withdrawal from China of this dynamic segment of the missionary force exposed the church to successive waves of persecution. Although many Chinese Christians were put to death and the congregation scattered, the church continued to manifest a "tough inward vitality" and kept growing.
 |
| The Qianlong Emperor, by Charles-Eloi Asselin (1743-1805) after Giuseppe Panzi. Louvre Museum. |
See also
- 19th Century Protestant Missions in China
- Cathedral of Saint Paul in Macau
- Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception in Hangzhou
- China and the Christian Impact, translation of Jacques Gernet's Chine et christianisme of 1982
- France-China relations
- History of the Jews in China
- Judaism in China
- List of Roman Catholic missionaries in China
- Medical missions in China
- Roman Catholicism in China
- Three Pillars of Chinese Catholicism
- Cornelius Wessels
Notes
The Jesuits, such as Johann Schreck, translated European technical books into Chinese.
Left image: a description of a windlass well, in Agostino Ramelli, 1588.
Right image: Description of a windlass well, in Diagrams and explanations of the wonderful machines of the Far West, 1627.
Left image: a description of a windlass well, in Agostino Ramelli, 1588.
Right image: Description of a windlass well, in Diagrams and explanations of the wonderful machines of the Far West, 1627.
- ^ Wigal, p.202
- ^ Mungello (2005), p. 37. Since Italians, Spaniards, Germans, Belgians, and Poles participated in missions too, the total of 920 probably only counts European Jesuits, and does not include Chinese members of the Society of Jesus.
- ^ Kenneth Scott, Christian Missions in China, p.83.
- ^ Article on the Jesuit cemetery in Beijing by journalist Ron Gluckman
- ^ Ruggieri, Ricci & Witek 2001, p. 151
- ^ a b Ruggieri, Ricci & Witek 2001, p. 153
- ^ George H. Dunne, Generation of Giants, p.28
- ^ Leonard M. Outerbride, The Lost Churches of China, p.85.
- ^ Ruggieri, Ricci & Witek 2001, p. 155
- ^ Johannes Beckmann, Dialogue with Chinese Religion, p.124-130.
- ^ George H. Dunne, Generation of Giants, p.44.
- ^ Mungello (1989), p. 49
- ^ 泰山“九莲菩萨”和“智上菩萨”考
- ^ Mungello (1989), p. 106-107
- ^ 清代中叶四川天主教传播方式之认识
- ^ Mungello (1989), p. 91
- ^ 南明永曆朝廷與天主教
- ^ 中西文化交流与西方早期汉学的兴起
- ^ Mungello (1989), p. 139
- ^ Eastern Magnificence and European Ingenuity: Clocks of Late Imperial China - Page 182 by Catherine Pagani (2001) Google Books
- ^ Mungello (1989), p. 139-140, 167
- ^ Mungello (1989), p. 167
- ^ Keevak, p.38
- ^ a b BBC
- ^ Patricia Buckley Ebrey, p 212
- ^ Ricci roundtable
- ^ Agustín Udías, p 53; quoted by Woods
- ^ 第八章 第二次教难前后
- ^ 志二十
- ^ Shenwen Li, p.235
- ^ John Parker, Windows into China: the Jesuits and their books, 1580-1730. Boston: Trustees of the Public Library of the City of Boston, 1978. p.25. ISBN 0-89073-050-4
- ^ John Parker, Windows into China, p. 25.
- ^ John Hobson, The Eastern origins of Western Civilization, pp. 194-195. ISBN 0-521-54724-5
- ^ See e.g. Martino Martini's detailed account in Martini Martinii Sinicae historiae decas prima : res a gentis origine ad Christum natum in extrema Asia, sive magno Sinarum imperio gestas complexa, 1659, p. 15 sq.
- ^ Du Halde, Jean-Baptiste (1735). Description géographique, historique, chronologique, politique et physique de l'empire de la Chine et de la Tartarie chinoise. Volume IV. Paris: P.G. Lemercier. There are numerous later editions as well, in French and English
- ^ Swerts, p.18[not in citation given]
- ^ Batalden, p.151
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: Jesuit China missions |
- Patricia Buckley Ebrey, The Cambridge Illustrated History of China. Cambridge, New York and Melbourne: Cambridge University Press, 1996. ISBN 0-521-43519-6.
- Agustín Udías, Searching the Heavens and the Earth: The History of Jesuit Observatories (Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2003)
- Lorry Swerts, Mon Van Genechten, Koen De Ridder, Mon Van Genechten (1903–1974): Flemish Missionary and Chinese Painter : Inculturation of Chinese Christian Art, Leuven University Press, 2002 ISBN 90-5867-222-0 ISBN 9789058672223
- Stephen K. Batalden, Kathleen Cann, John Dean, Sowing the word: the cultural impact of the British and Foreign Bible Society, 1804-2004 Sheffield Phoenix Press, 2004 ISBN 1-905048-08-4 ISBN 9781905048083
- Thomas Woods, How the Catholic Church Built Western Civilization, (Washington, DC: Regenery, 2005), ISBN 0-89526-038-7
- Wigal, Donald (2000) Historic Maritime Maps, Parkstone Press, New York, ISBN 1-85995-750-1
- Mungello, David E. (1989). Curious Land: Jesuit Accommodation and the Origins of Sinology. University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 0-8248-1219-0.
- Mungello, David E. (2005). The Great Encounter of China and the West, 1500-1800. Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 0-7425-3815-X.
- Ruggieri, Michele; Ricci, Matteo; Witek, John W. (2001), Dicionário Português-Chinês : 葡漢詞典 (Pu-Han Cidian) : Portuguese-Chinese dictionary, Biblioteca Nacional, pp. 151–157, ISBN 972-565-298-3 (Detailed account of the early years of the mission)
|
||




No comments:
Post a Comment
Comments always welcome!